The Best General Characteristic Describing Pleural Plaques Includes
However these terms have different meanings. Calcification of pleural plaques is seen in 10 to 15 of cases.

The Role Of Imaging In Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma An Update After The 2018 Bts Guidelines Clinical Radiology
Inside your chest there are two thin layers of cells - called the pleura or pleural membrane.
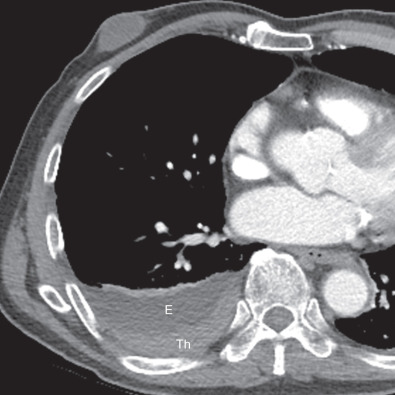
. Two series report that patients with plaques tend to have a marked increase in the high aspect ratio amphiboles amosite and crocidolite but no other fiber types. The pleura is a two-layered membrane surrounding the lungs and lining the inside of the rib cage. Bilateral well defined irregular shadows that are as dense as the bones.
These localized scars have collagen fiber deposits and normally form after there has been exposure to asbestos fibers. Non-malignant asbestos pleural effusions. They are the most common sign of asbestos damage to the chest cavity but may not develop for decades after the exposure.
The characteristic presentation of pleural plaques on high-resolution CT consists of circumscribed areas of pleural thickening separated from the underlying ribs and extrapleural soft tissues by a thin layer of fat. Retired dock worker with history of multiple exposures to asbestos. Pleural plaques do not become malignant.
External examination revealed the presence of yellow discolouration affecting the finger- and toenails Figure 2 along with bilateral lower leg oedemaExamination of the respiratory system showed extensive bilateral pleural adhesions diffuse visceral pleural thickening and parietal pleural plaques Figure 3. Thus radiographic diagnosis requires careful evaluation. Patients with pleural plaques are asymptomatic and the plaques are most useful as a marker of asbestos exposure.
Pleural plaques are localized scars in the lungs. Pleural plaques are the most common sign of asbestos exposure. The symptoms of pleural plaques may include dry coughing shortness of breath fatigue weight loss lower Back pain sweating muscle weakness and fever.
Pleural plaques are sometimes referred to as hyaline pleural plaques. Asbestos related pleural plaques. Number and types of asbestos fibers in subjects with pleural plaques.
Asbestosis mimics idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis radiographically especially in CT. The chalky thick areas are known as pleural plaques. The inner layer covers your lungs and the outer layer lines the inside of your rib cage.
This is because they. Chronic mild shortness of breath. If you have been exposed to asbestos its common for areas of the pleura to become thickened.
Many people have developed a huge fear of asbestos and quite rightly so. They are grey-white areas of thickened tissue in the lung lining pleura. Bilateral calcified asbestos related pleural plaques.
Pleural plaques were defined as focal areas of pleural thickening with soft tissue attenuation which could contain calcification typically located on the posterior wall of the lower half of the pleural spaces often in the paravertebral regions on the anterior wall between the third and the fifth costal interspaces andor on the diaphragmatic pleura. However there are a few rare cases in which pleural plaques are found near. From the history of breathlessness and the chest X-ray with characteristic pleural plaques and interstitial fibrosis it suggests that the patient has asbestosis.
It is a mineral that if left undisturbed provides various industries with a range of benefits. Pleural plaques are evidence of past asbestos exposure and it is the asbestos exposure itself that can cause more severe disease. Differential diagnoses of pleural nodules include pleural dissemination of malignant disease malignant pleural mesothelioma malignant lymphoma fibrous.
Pleural plaques are the most common manifestation of asbestos inhalation and occur 2030 years after first exposure. Pleural plaques that form because of asbestos fibers are normally found in the parietal pleura the lining of the inner wall of the chest. Pleural plaques are seen in 314 of dockyard workers and in 58 of insulation workers.
However our results can be contextualized in relation with the prevalence of pleural plaques in the general population reported in the literature that ranges from 002 to 75 1819 20 and. Rib companion shadows fat intercostal vessels and muscles can appear as plaques. Rounded atelectasis folded lung.
What are pleural plaques and their etiologies -pearly-white smooth or nodular plaques usually bilateral that typically occurs on the parietal and diaphragmatic pleura -usually seen 10-20 years after exposure to asbestos but may also be found in up to 15 of the general population who have no history of exposure to asbestos therefore pleural plaques are not a predictor of. Asbestos fibers and pleural plaques in a general autopsy population. Chest x-rays show large false negative and varying false positive rates.
Hence the most probable histopathological description is the presence of ferruginous bodies in. On radiography pleural plaques manifest as discontinuous areas of pleural thickening that may be calcified or noncalcified with incomplete borders and characteristically distributed. Less Common Radiologic Manifestations.
The plaques are composed of fibrohyaline tissue and form within the parietal pleura manifesting with characteristic radiographic and CT findings Fig. Pleural plaques are areas of thickened tissue in the pleura around the lungs. The important distinguishing point is that asbestosis begins more centrally and dissipates peripherally following a centrifugal pattern.
Plaques do not typically cause symptoms and may or may not develop into malignant pleural mesothelioma. It is very common for areas of this membrane to become thickened and to accumulate a chalky material If one has been exposed to. A Common Result of Asbestos Exposure.
Asbestos related pleural thickening and detection. Each layer is about as thin as the skin of a balloon. In this section we explain what pleural plaques are.
The terms calcification and thickening often were used as synonymous with plaques. Pleural thickening and calcified pleural plaques in tomography are the hallmarks of the disease. A postmortem examination was performed.
Asbestos related pleural thickening is a fibrous layer of tissue covering a significant portion of the pleura.

Pleural Plaque Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Pleural Plaque Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Diagnosis Of Tuberculous Pleural Effusions A Review Respiratory Medicine

Diagnostic Utility And Clinical Application Of Imaging For Pleural Space Infections Chest

Pleural Effusion Diagnosis Treatment And Management Abstract Europe Pmc

Diagnostic Utility And Clinical Application Of Imaging For Pleural Space Infections Chest

Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease Copd Emphysema Radiology Imaging Respiratory Therapy Respiratory Care

Pleural Neoplasms Radiology Key
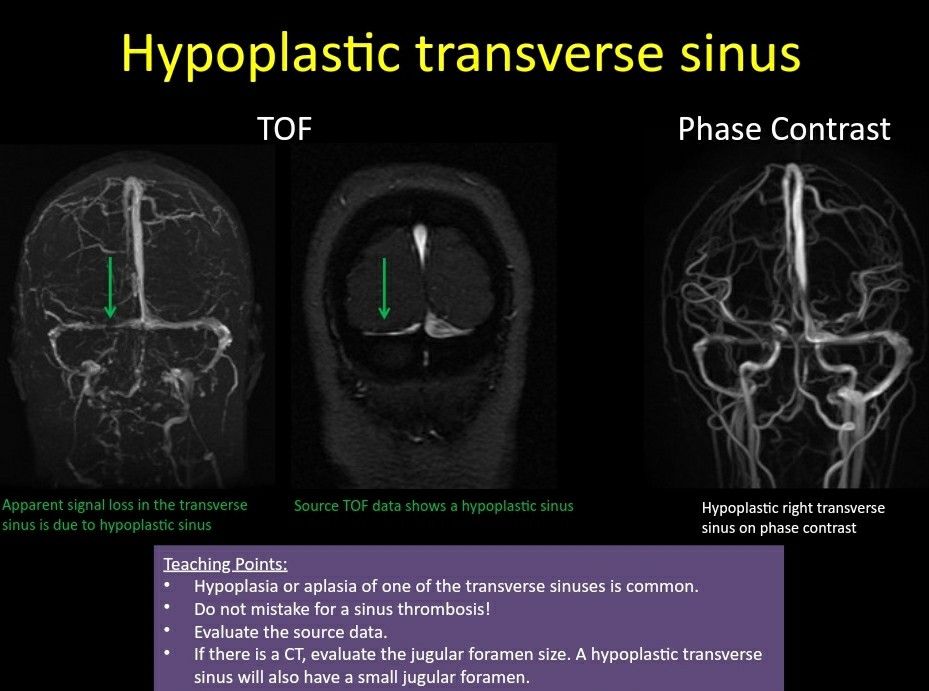
Unlike Transverse Sinus Thrombosis That Will Display An Abnormal Signal In T1 T2 Images While Flow Void Remains In A Hypoplas Sinusitis Thrombosis Radiology

Diagnostic Utility And Clinical Application Of Imaging For Pleural Space Infections Chest
Diagnostics Free Full Text Diagnostics In Pleural Disease Html

The Frequency Risk Factors And Management Of Complications From Pleural Procedures Chest

Progressive Massive Fibrosis Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org Human Body Systems Radiology Human Body Anatomy
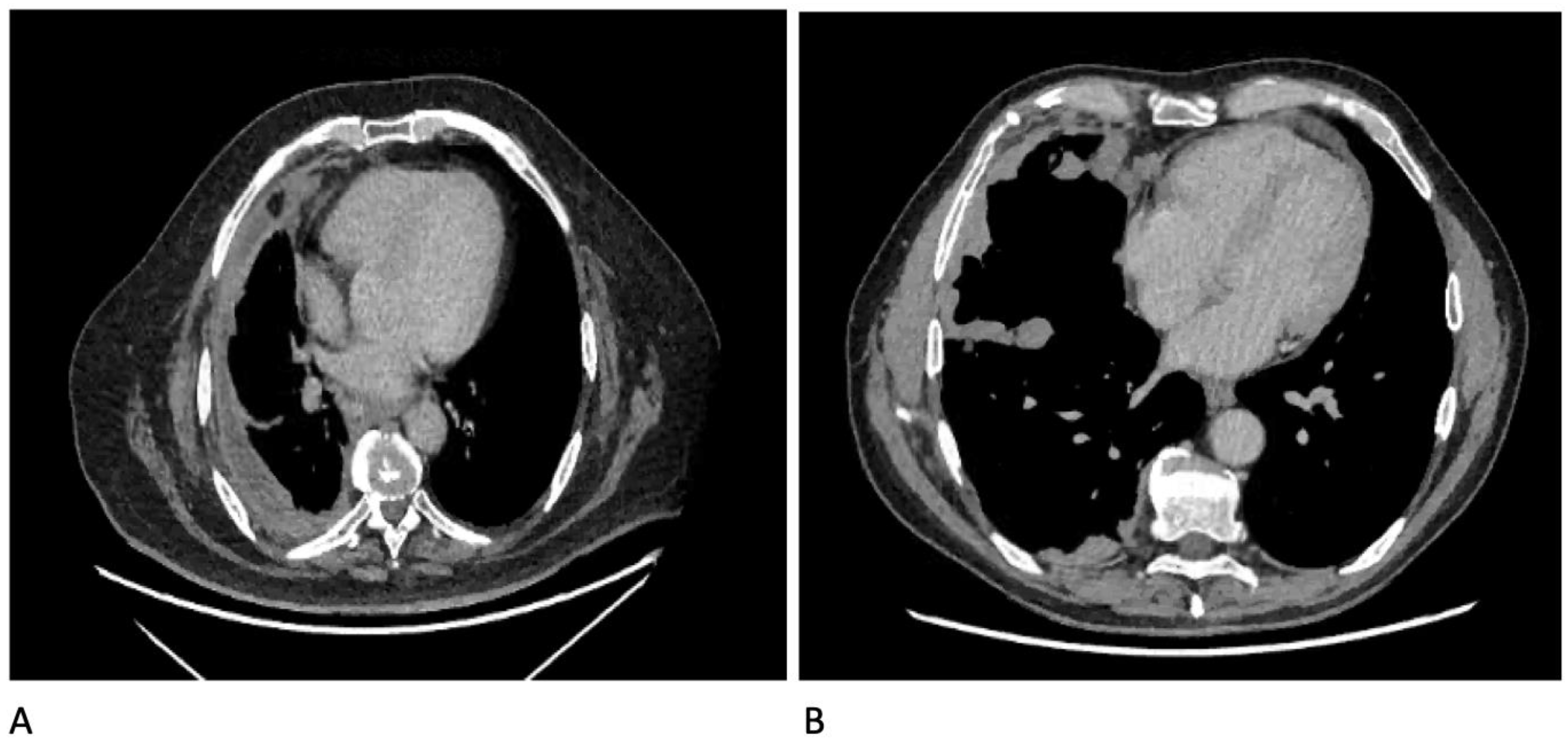
Diagnostics Free Full Text Diagnostics In Pleural Disease Html

File Signs And Symptoms Of Hypothyroidism Png Hypothyroidism Symptoms Hypothyroidism Treatment Thyroid Treatment
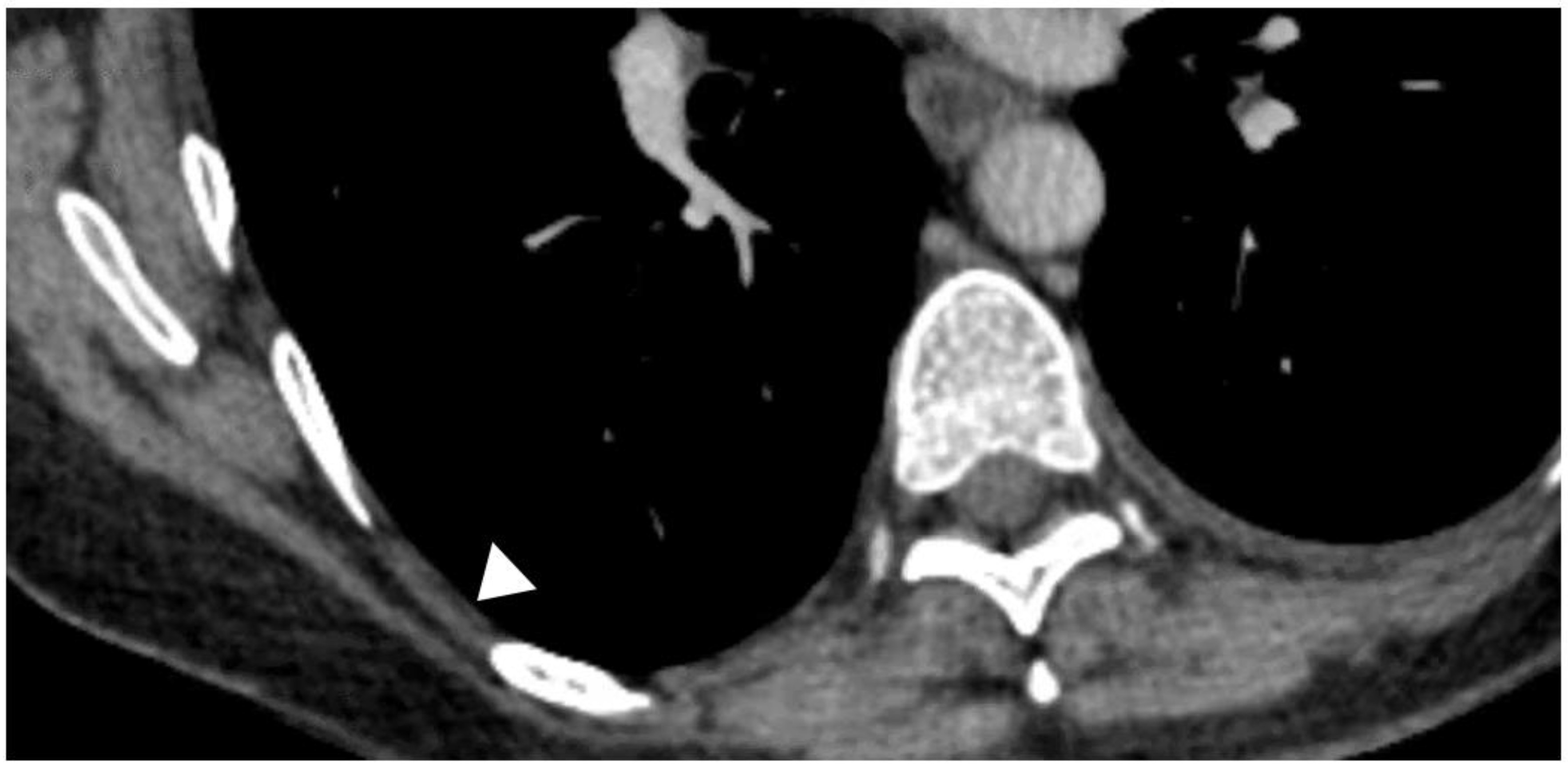
Diagnostics Free Full Text Diagnostics In Pleural Disease Html
Comments
Post a Comment